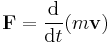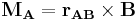Moment (physics)
"Principle of Moments" redirects here. For the
Robert Plant album, see The Principle of Moments. For a more abstract concept of moments that evolved from this concept of physics, see
Moment (mathematics).
In physics, the term "moment" can refer to many different concepts:
- Moment of force (often just moment) is the tendency of a force to twist or rotate an object; see the article torque for details. This is an important, basic concept in engineering and physics. (Note: In mechanical and civil engineering, "moment" and "torque" have different meanings, while in physics they are synonyms. See the discussion in the "torque" article, or the article couple (mechanics).)
- Moment arm is a quantity used when calculating moments of force. See the article torque.
- The Principle of moments is a theorem concerning moments or force. See the article torque.
- A pure moment is a special type of moment of force. See the article couple (mechanics).
- Moment of a vector is a generalization of the moment of force. The moment M of a vector B about the point A is
-
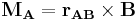
- where
-
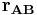 is the vector from point A to the position where quantity B is applied.
is the vector from point A to the position where quantity B is applied.- × represents the cross product of the vectors.
- Thus M can be referred to as "the moment M with respect to the axis that goes through the point A", or simply "the moment M around A". If A is the origin, or, informally, if the axis involved is clear from context, one often omits A and says simply moment.
- When B is the force, the moment of force is the torque as defined above.
- Moment of inertia (
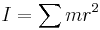 ) is analogous to mass in discussions of rotational motion.
) is analogous to mass in discussions of rotational motion.
- Moment of momentum or angular momentum (
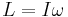 ) is the rotational analog of momentum.
) is the rotational analog of momentum.
- Magnetic moment (
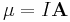 ) is a dipole moment measuring the strength and direction of a magnetic source.
) is a dipole moment measuring the strength and direction of a magnetic source.
- Electric dipole moment is a dipole moment measuring the charge difference and direction between two or more charges. For example, the electric dipole moment between a change of -q and q separated by a distance of d is (
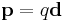 )
)
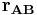 is the vector from point A to the position where quantity B is applied.
is the vector from point A to the position where quantity B is applied.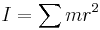 ) is analogous to mass in discussions of rotational motion.
) is analogous to mass in discussions of rotational motion.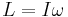 ) is the rotational analog of momentum.
) is the rotational analog of momentum.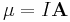 ) is a dipole moment measuring the strength and direction of a magnetic source.
) is a dipole moment measuring the strength and direction of a magnetic source.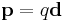 )
)